Is the Biodegradability of PLA Coated Paper Promising?
What is PLA Coated Paper and How is It Made?
[Keyword Cluster]: PLA coated paper, biodegradable PLA-coated paper
Introduction:
PLA coated paper is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional coatings that offers biodegradability, water resistance, and durability. In this section, we will explore what PLA (Polylactic Acid) is, how PLA coated paper is manufactured, and why it is a popular choice for coating paper products.
What is PLA?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is a thermoplastic material that can be made into various forms, including filaments for 3D printing, packaging materials, and coatings for paper products.
Composition of PLA:
PLA is composed of lactic acid monomers, which are obtained through the fermentation of sugars found in plants. Lactic acid monomers are polymerized to form a long-chain polymer known as PLA. The composition of PLA can vary depending on the source material used, but it is generally made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
Sources of PLA:
PLA can be derived from various plant-based sources, with the most common being corn starch and sugarcane. Corn starch is broken down into glucose molecules, which are then fermented by specific bacteria to produce lactic acid. Sugarcane can also be used as a source for lactic acid production, reducing the reliance on corn-based resources.
How is PLA Coated Paper Manufactured?
The manufacturing process of PLA coated paper involves applying a thin layer of PLA onto the surface of paper. This coating provides the paper with enhanced properties such as water resistance and durability.
Coating Process:
The coating process begins by preparing a PLA solution, which can be achieved by dissolving PLA pellets in a solvent. The PLA solution is then applied to the paper surface using various methods, such as roll coating, blade coating, or extrusion coating. The coated paper is then dried to remove any remaining solvent, resulting in a PLA coated paper product.
Differences between PLA Coating and Traditional Polyethylene Coating:
PLA coating offers several advantages over traditional coatings, such as polyethylene (PE). Unlike PE, which is derived from petroleum-based sources, PLA is made from renewable plant-based materials. PLA coating provides similar or even better water resistance and durability compared to PE coating, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative.
Why Choose PLA for Coating Paper?
PLA coated paper offers various benefits over traditional plastics and coatings. Here are some reasons why PLA is a popular choice for coating paper products:
Benefits of using PLA over traditional plastics:
- Biodegradability: PLA is fully biodegradable under specific conditions, such as in industrial composting facilities. This reduces the environmental impact and potential for plastic pollution.
- Renewable Resources: PLA is made from renewable plant-based sources, reducing the dependence on fossil fuels.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: PLA emits fewer greenhouse gases during production compared to petroleum-based plastics.
- Safe for Food Contact: PLA is non-toxic and approved for food contact, making it a safe choice for food packaging.
- Versatility: PLA can be used for various paper products, providing durability and water resistance.
Properties imparted by PLA coating:
- Water Resistance: PLA coating provides a hydrophobic barrier, preventing moisture from penetrating the paper surface.
- Durability: The PLA coating enhances the strength and durability of the paper, making it suitable for various applications.
In conclusion, PLA coated paper offers an eco-friendly and sustainable option for paper coating. Its biodegradability, water resistance, and durability make it a suitable choice for food packaging and other applications. By using PLA coated paper, companies can reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Biodegradability of PLA Coated Paper and its Environmental Impacts
Introduction
PLA coated paper is an eco-friendly packaging option that has gained significant attention in recent years. It is made from polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable material derived from renewable plant resources like corn starch and sugarcane. In this article, we will delve into the environmental impacts of PLA coated paper and explore its biodegradability, comparing it to other coating materials. We will also discuss the certifications and standards that validate its biodegradability claims.
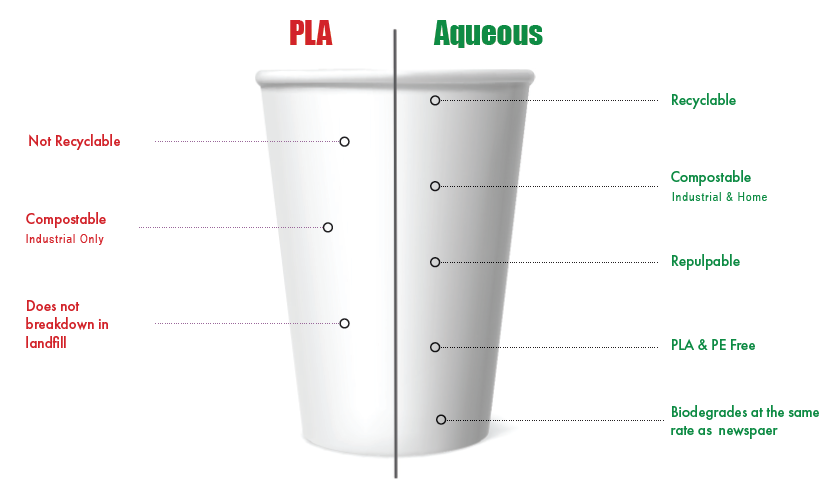
Is PLA Coated Paper Truly Biodegradable?
PLA coated paper is often marketed as biodegradable. However, it is important to understand the conditions required for its biodegradability. PLA requires specific conditions, such as temperatures of about 58°C (136.4°F), high humidity, and the presence of certain microbes, which are typically found in industrial composting facilities. In these controlled environments, PLA coated paper can biodegrade within a timeframe of 45-90 days.
It is essential to note that PLA does not degrade under natural environmental conditions like backyard composting or in landfills. Without the presence of the specific conditions required for biodegradation, PLA coated paper can persist in the environment for an extended period of time. In natural environments such as soil or marine settings, it can take up to 1000 years to decompose completely.
Comparing PLA Coated Paper to Other Coating Materials
When assessing the environmental impact of PLA coated paper, it is crucial to compare it to traditional petroleum-based coatings, like polyethylene (PE). PLA offers several environmental benefits over these traditional coatings. Firstly, PLA is derived from renewable plant-based sources, reducing reliance on finite resources and minimizing carbon emissions during production.
A significant advantage of PLA coated paper is the reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional coatings. PLA emits fewer greenhouse gases during its production process, contributing to the reduction of overall carbon emissions. Additionally, PLA coated paper can be recycled, minimizing waste and further reducing environmental impact.
Certification and Standards for Biodegradability
To validate the biodegradability claims of PLA coated paper, certain certifications and standards have been established. The most commonly recognized standards are ASTM D6400 (USA) and EN 13432 (Europe). These standards specify the conditions under which the material should biodegrade, ensuring consistency and reliability in assessing its environmental impact.
Certifications are essential in validating environmental claims for PLA coated paper. They provide assurance to consumers that the product meets specific criteria for biodegradability. When choosing PLA coated paper, it is important to look for certifications that indicate compliance with these standards, ensuring that the product holds up to its sustainable claims.
How Long Does it Take for PLA Coated Paper to Decompose?
Under industrial composting conditions, PLA coated paper can biodegrade within 45-90 days. However, it is important to recognize that this timeframe is dependent on the specific conditions in the composting facility, such as temperature and humidity levels. Without these conditions, the decomposition process may be significantly delayed or hindered.
In natural environments, where the necessary conditions for biodegradation are absent, PLA coated paper can take up to 1000 years to decompose completely. This highlights the importance of proper waste management and disposal practices to ensure that PLA coated paper reaches composting facilities where it can biodegrade appropriately.
Can PLA Coated Paper be Composted at Home?
It is not recommended to compost PLA coated paper at home. As mentioned earlier, PLA requires specific conditions, such as high temperatures and the presence of certain microbes, which are typically found in industrial composting facilities. Backyard composting does not provide these necessary conditions for efficient biodegradation of PLA coated paper.
To minimize the environmental impact of PLA coated paper, it is essential to dispose of it in appropriate waste streams that can facilitate its proper degradation, such as industrial composting facilities that meet the necessary conditions for PLA biodegradation.
In conclusion, PLA coated paper offers significant environmental benefits compared to traditional petroleum-based coatings. It is important to understand the conditions required for its biodegradability and the certifications that validate its environmental claims. By disposing of PLA coated paper in appropriate waste streams and supporting industrial composting facilities, we can maximize its environmental benefits and contribute to a more sustainable future.
References:
[1] Biodegradable Products Institute. (n.d.). "ASTM D6400 & EN13432: Why You Need to Look For These Certifications When You Choose Compostable Products." Retrived from https://bpiworld.org/PLA-FAQs
[2] Plastic Oceans International. (2021). "Polylactic Acid (PLA) Bioplastics." Retrieved from https://plasticoceans.org/polylactic-acid-pla-bioplastics/
What are the Practical Applications and Future Trends of PLA Coated Paper?
PLA coated paper, also known as polylactic acid coated paper, is gaining popularity as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic-coated paper. In this section, we will explore the practical applications of PLA coated paper and discuss emerging trends and future advancements in this field.
Current Uses of PLA Coated Paper
PLA coated paper finds its most common applications in the food packaging industry. Its moisture and grease resistance properties make it an ideal choice for food containers, cups, bowls, and takeaway containers. Many fast-food chains and restaurants are switching to PLA coated paper packaging as a more sustainable option.
In addition to food packaging, PLA coated paper is used in non-food applications as well. It is used in the manufacturing of paperboard and packaging for non-perishable items like household products, electronics, and personal care items. The versatility of PLA coated paper makes it suitable for various shapes and sizes, catering to different industries.
Case Studies and Industry Examples
Numerous companies across the globe have adopted PLA coated paper and experienced positive results in terms of sustainability, customer acceptance, and brand reputation. Let's take a look at a few examples:
- Company A – A leading fast-food chain replaced their traditional plastic-coated cups with PLA coated paper cups. This switch significantly reduced their carbon footprint and waste generation. They reported positive feedback from customers, who appreciated the environmentally friendly approach.
- Company B – A major packaging manufacturer started producing PLA coated paper containers for various industries. They observed that their clients, especially those in the food industry, preferred PLA coated paper packaging due to its sustainability benefits. Not only did it improve their brand image, but it also contributed to reducing their overall environmental impact.
These case studies illustrate the successful adoption of PLA coated paper by businesses across different sectors. By implementing sustainable solutions, these companies have not only reduced their environmental impact but also gained a competitive edge in the market.
Emerging Trends and Research in PLA Coated Paper
As the demand for sustainable packaging continues to grow, innovations in PLA coating technologies are on the rise. Researchers and manufacturers are constantly exploring new methods to improve the biodegradability, recyclability, and overall performance of PLA coated paper.
- Advancements in Biodegradability: Scientists are working on enhancing the biodegradability of PLA coated paper by developing coatings that can decompose in a wider range of environments, including home composting and natural settings. This would significantly reduce the time required for decomposition and make PLA coated paper a more versatile and eco-friendly option.
- Recycling Innovations: Recycling PLA coated paper poses unique challenges due to its specific composition. Researchers are studying methods to effectively separate PLA from other plastics during the recycling process. This will allow for more efficient recycling, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and further promoting the circular economy.
- Bio-based PLA Coatings: There is ongoing research into developing PLA coatings using bio-based materials, such as waste from agricultural industries or other renewable sources. This approach would enhance the sustainability of PLA coated paper by reducing its reliance on fossil fuel-based resources.
- Improved Performance: In order to expand the applications of PLA coated paper, researchers are focusing on enhancing its performance characteristics, such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and barrier properties. This will allow for broader usage across industries and provide more sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic coatings.
These emerging trends and ongoing research signify the continuous efforts being made to improve PLA coated paper and make it more sustainable and practical for a variety of applications.
In conclusion, PLA coated paper is finding widespread use in the food packaging industry and beyond. Its biodegradability and renewable composition make it an environmentally friendly choice. Companies adopting PLA coated paper have seen positive results in terms of sustainability and customer acceptance. Furthermore, ongoing research and innovations in PLA coating technologies are paving the way for future advancements and a more sustainable future.
FAQs about Biodegradability of PLA Coated Paper
What is PLA Coated Paper?
A: PLA coated paper is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional coatings that offers biodegradability, water resistance, and durability.
How is PLA Coated Paper Made?
A: The manufacturing process of PLA coated paper involves applying a thin layer of Polylactic Acid (PLA) onto the surface of paper, providing enhanced properties such as water resistance and durability.
Is PLA Coated Paper Truly Biodegradable?
A: PLA coated paper is often marketed as biodegradable but requires specific conditions like high temperatures, humidity, and certain microbes found in industrial composting facilities to decompose within 45-90 days.
Can PLA Coated Paper be Composted at Home?
A: It is not recommended to compost PLA coated paper at home because it requires specific conditions such as high temperatures and the presence of certain microbes, typically found in industrial composting facilities.
What are the Benefits of Using PLA Coated Paper?
A: PLA coated paper offers benefits such as biodegradability under specific conditions, being made from renewable plant-based resources, emitting fewer greenhouse gases during production, and being safe for food contact.
PLA coated paper is a game-changer for eco-friendly packaging. We explored everything from its production to environmental impact and future uses. It's clear that PLA offers many benefits over traditional plastics. The eco-certifications ensure you can trust its biodegradability. With advancements on the horizon, PLA's role in sustainable packaging will only grow. Keep an eye on this innovative material—it’s shaping the future of green packaging!