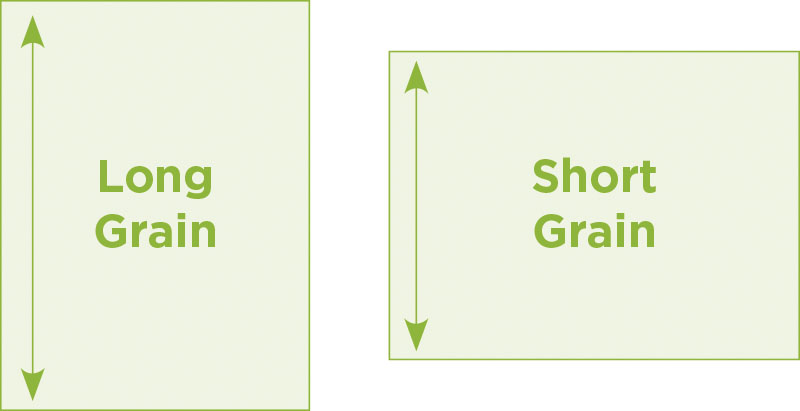
Short Grain vs Long Grain Paper: Which is better?
Title: Short Grain vs Long Grain Paper: Understanding the Differences
Section 1: Short Grain vs Long Grain Paper Overview
What is the difference between short grain paper and long grain paper?
Short grain paper and long grain paper differ in the direction in which the fibers spread during the paper-making process. Short grain paper has fibers that run across the shorter side of the sheet, while long grain paper has fibers that run across the longer side.
How does paper grain direction impact printing and bookbinding?
Paper grain direction plays a crucial role in printing and bookbinding processes. When folding paper against the grain, it can lead to less appealing folds and require scoring beforehand. For bookbinding, it is important to align the paper grain direction with the book binding edge to ensure consistency and prevent pages from sticking out.
Short grain paper characteristics and uses
Short grain paper has its fibers running along the shortest side of the sheet. Some of the characteristics of short grain paper include:
- Stiffness and stability: Short grain paper is known for its high stiffness and stability, making it ideal for applications that require durability, such as packaging materials.
- Smooth surface: Short grain paper has a smooth surface that allows for excellent print quality and image sharpness. It is often used in printing projects that require high-quality finishes.
- Folding ease: Due to its grain direction, short grain paper is easier to fold along the shorter side. This makes it a preferred choice for projects that involve folding, such as brochures, flyers, and cards.
Long grain paper characteristics and uses
Long grain paper has its fibers running along the longest side of the sheet. Here are some key characteristics of long grain paper:
- Flexibility: Long grain paper is more flexible compared to short grain paper. This makes it suitable for projects that require intricate folding and complex structures.
- Large format printing: Long grain paper is often used in large format printing, such as posters, banners, and architectural drawings. Its flexibility allows for smooth printing and handling.
- Bookbinding: Long grain paper is commonly used in bookbinding, particularly in the production of mass-produced books. Its grain direction aligns well with the binding edge, ensuring a seamless and professional finish.
Advantages and disadvantages of short grain paper
Advantages:
- High stiffness and stability
- Smooth surface for excellent print quality
- Easy folding along the shorter side
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility for intricate folding and complex structures
Advantages and disadvantages of long grain paper
Advantages:
- Flexibility for intricate folding and complex structures
- Suitable for large format printing
- Ideal for bookbinding with consistent binding edge alignment
Disadvantages:
- Less stiffness and stability compared to short grain paper
In summary, understanding the differences between short grain paper and long grain paper is crucial for various paper applications, including printing and bookbinding. Short grain paper offers high stiffness and stability with easy folding, while long grain paper provides flexibility for intricate folds and large format printing. Consider the specific needs of your project to choose the right paper grain direction for optimal results.
Identifying Paper Grain Direction
In the world of bookbinding and printing, understanding paper grain direction is crucial to achieving optimal results. Paper grain direction refers to the direction in which the fibers spread during the papermaking process. There are two main types of grain direction: short grain and long grain. In this section, we will explore why paper grain direction is important, methods to determine paper grain direction, and the significance of aligning paper grain direction with book binding edge and printing.
Why is paper grain direction important in bookbinding and printing?
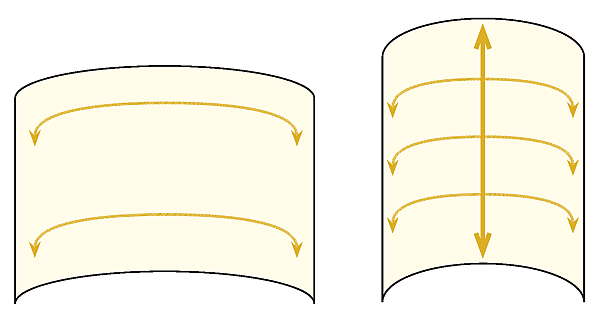
Paper grain direction plays a significant role in bookbinding and printing for several reasons. First, it affects how paper reacts to mechanical actions such as folding, scoring, and binding. When paper is folded against the grain, it tends to result in less appealing folds and may require scoring beforehand. When folded with the grain, the paper folds more smoothly and cleanly.
Second, when binding a book, it is important to align the paper grain direction with the book binding edge. When the grain direction is consistent throughout the book, the pages lay flat and do not stick out. This ensures a professional and visually appealing end product.
Third, the implications of incorrect grain direction on the printing process can be significant. Printing on paper with the wrong grain direction may result in issues such as wrinkling, misfeeds, and poor image quality. It is essential to align the grain direction with the printing process to achieve optimal results.
Methods to Determine Paper Grain Direction
There are several methods to determine the grain direction of paper.
- Fold Method: The Fold Method is the most straightforward way to identify paper grain direction. By folding a sheet of paper in both directions, one will notice that it either folds more easily in one direction or there is slightly more resistance when folding against the grain. The direction with more resistance indicates the grain direction.
- Water Method: The Water Method involves wetting a sheet of paper and observing how it curls as it dries. When paper is wet, it expands and curves along the grain direction. By noting the direction of the curl, one can determine the grain direction.
- Packaging Labeling: Many paper companies provide information about grain direction on their packaging labels. They may underline the grain direction on paper sizes or state it as "short grain" or "long grain" directly on the packaging. Checking the packaging labeling can be a straightforward way to identify grain direction.
- Feeling and Tear Test: Another way to detect paper grain direction is by feeling the paper with your fingers. Papers usually have a smoother side, which indicates the direction in which the fibers align. Additionally, conducting a tear test can also help determine the grain direction. When tearing the paper, it will be easier to tear along the grain direction compared to tearing against it.
Significance of Aligning Paper Grain Direction with Book Binding Edge
Aligning the paper grain direction with the book binding edge is essential in bookbinding. When the grain direction of the paper is parallel to the binding edge, it enhances the stability and durability of the book. Binding a book against the grain can lead to issues such as spine warping and gusseting.
The choice of paper grain direction also depends on the type of bookbinding method used. When using methods such as perfect binding or saddle stitching, where the paper is folded into sections, it is ideal to use paper with short grain. Short grain paper, with its fibers running across the shortest side of the sheet, provides easier and more precise folding of the sections.
Printing Implications of Incorrect Grain Direction
Printing on paper with the wrong grain direction can result in a variety of issues. One common problem is wrinkling, especially when using heavier paper. The fibers in the paper expand or contract more across the grain, causing the paper to warp or wrinkle during the printing process.
Misfeeds can also occur when the grain direction is not aligned properly with the printer's feed direction. This can lead to paper jams and delays in the printing process. Additionally, printing against the grain can result in poor image quality, such as reduced color vibrancy and less sharpness in printed images.
How to Prevent Printing Issues by Aligning Paper Grain Direction Correctly
To prevent potential printing issues, it is crucial to align the paper grain direction correctly. Here are a few tips to ensure proper alignment:
- Check packaging labeling: Always refer to the packaging labeling for information on grain direction. This will help identify the correct orientation of the paper fibers.
- Choose the right paper: When selecting paper for a print project, consider the desired grain direction for optimal results. Ensure that the chosen paper has the correct grain direction for the specific printing method and equipment being used.
- Contact paper manufacturers: If purchasing paper online and the grain direction is not specified, it may be necessary to contact the paper manufacturer directly. Requesting spec sheets or additional information on grain direction can ensure that the correct paper is chosen for the project.
- Perform test prints: Before running a large print job, it is advisable to conduct test prints with the chosen paper. This allows for any potential issues related to grain direction to be identified and addressed beforehand.
By taking these preventive measures, one can avoid common printing issues associated with incorrect grain direction and achieve professional-looking print materials.
Importance of Choosing the Right Paper Grain Direction for Optimal Print Results
Selecting the appropriate paper grain direction is essential for producing high-quality print materials. Whether it is short grain or long grain, understanding how grain direction affects the folding, scoring, binding, and printing processes is crucial. By aligning the paper grain direction correctly, print professionals can ensure smooth production workflows, minimize printing issues, and achieve optimal results in terms of color vibrancy, image sharpness, and overall appearance.
In the next section, we will explore the practical applications of short and long grain paper in bookbinding and printing, along with best practices for utilizing them effectively.
Practical Applications of Short and Long Grain Paper
Short grain paper and long grain paper have different characteristics and properties that make them suitable for various applications in the fields of bookbinding and printing. Understanding the differences in paper handling and choosing the right paper grain direction is essential for achieving optimal results in these industries. In this section, we will explore the practical applications of short grain paper and long grain paper, as well as the best practices and common mistakes to avoid.
Use Cases of Short Grain Paper in Bookbinding and Printing
Short grain paper, with its grain running along the shortest side of the sheet, is commonly used in bookbinding and printing for various purposes. The shorter grain direction allows for easier folding and binding, making it ideal for creating book sections and pamphlets. It is often used in the production of paperback books, leaflets, and brochures. Short grain paper is also favored for projects that require frequent folding or bending, as it offers better resistance to creasing.
Use Cases of Long Grain Paper in Bookbinding and Printing
On the other hand, long grain paper has its grain running along the longest side of the sheet. This type of paper is commonly used for larger, more durable projects such as hardcover books, notebooks, and catalogs. The longer grain direction provides better stability and strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Long grain paper is also preferred for projects that require finer finishes, as it offers smoother folds and better resistance to cracking.
Differences in Paper Handling for Short and Long Grain Paper
Handling short grain paper and long grain paper requires different techniques due to the variations in their grain direction. When working with short grain paper, it is important to fold and score the paper with the grain to achieve cleaner and more appealing folds. Folding against the grain can result in creases and less professional-looking results. On the other hand, long grain paper should be folded and scored against the grain for optimal results.
Choosing the Right Paper Grain Direction for Specific Projects
Choosing the correct paper grain direction is crucial for achieving the desired outcome in bookbinding and printing projects. When selecting paper for a project, consider the size, purpose, and desired finish. For projects that require frequent folding and bending, short grain paper is recommended. On the other hand, for projects that require durability and a premium finish, long grain paper is the better choice.
How Grain Direction Affects Folding, Scoring, and Binding in Bookmaking
Grain direction plays a significant role in bookmaking, particularly when it comes to folding, scoring, and binding. Folding paper against the grain can result in less appealing folds and requires additional measures such as scoring to prevent cracking. Binding should be done parallel to the grain to avoid spine warping and gusseting, ensuring a clean and professional-looking finish. By understanding the impact of grain direction on bookmaking processes, one can achieve better results in the final product.
Best Practices for Utilizing Short Grain and Long Grain Paper in Different Scenarios
To make the most of short grain and long grain paper, it is important to follow best practices in their utilization. Some best practices include:
- Understanding project requirements: Determine the specific needs of the project to select the appropriate paper grain direction.
- Testing paper grain direction: Use methods such as the Fold Method or the Water Method to determine the grain direction of the paper before starting the project.
- Aligning grain direction for binding: Ensure that the grain direction of the paper aligns with the book binding edge to prevent pages from sticking out and to maintain consistency.
- Considering paper weight: Heavier paper requires careful consideration of grain direction, as it can accentuate imperfections if not aligned correctly.
- Consulting paper manufacturers: If unsure about the grain direction of a particular paper, reach out to the paper manufacturer for specifications and information.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with Short and Long Grain Paper
When working with short grain paper and long grain paper, there are some common mistakes that should be avoided:
- Folding against the grain: Folding against the grain can result in creasing and less appealing folds. Always fold and score with the grain to achieve better results.
- Incorrect binding alignment: Binding parallel to the grain is crucial to prevent issues such as spine warping and gusseting. Ensure the grain direction is aligned correctly for binding.
- Neglecting paper weight: Paper weight affects how imperfections are shown. Consider the weight of the paper and choose the appropriate grain direction accordingly.
- Failure to test grain direction: Before starting a project, it is important to test the grain direction of the paper to ensure it aligns with the desired outcome.
- Ignoring manufacturer specifications: If in doubt about the grain direction of a particular paper, refer to the manufacturer's specifications for guidance.
By avoiding these common mistakes and following best practices, one can ensure smooth and successful results when working with short grain paper and long grain paper in bookbinding and printing projects.
Stay tuned for the next section where we will delve into additional aspects related to short grain and long grain paper.
Review Summary:
In this section, we explored the practical applications of short grain paper and long grain paper in bookbinding and printing. We discussed the use cases of each type of paper, the differences in paper handling, and the importance of choosing the right grain direction for specific projects. Additionally, we provided best practices and highlighted common mistakes to avoid when working with short grain and long grain paper. By understanding and implementing these guidelines, one can achieve optimal results in various bookmaking and printing scenarios.
FAQs about Short Grain vs Long Grain Paper
What is the difference between short grain paper and long grain paper?
To differentiate between short grain paper and long grain paper, consider the direction in which the fibers spread during the paper-making process. Short grain paper has fibers running along the shorter side, while long grain paper has fibers along the longer side.
How does paper grain direction impact printing and bookbinding?
Paper grain direction is crucial in printing and bookbinding processes due to how it affects folding, scoring, and binding. Folding against the grain may lead to less appealing results and scoring requirements, while aligning the grain direction in bookbinding ensures a professional finish.
What are the characteristics and uses of short grain paper?
With its fibers running along the shortest side, short grain paper boasts stiffness and stability, a smooth surface for quality prints, and ease of folding along the shorter side. It is commonly used for applications requiring durability and folding, like packaging materials and printed projects.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of long grain paper?
Long grain paper, with fibers along the longest side, offers flexibility for intricate folding and large format printing, making it ideal for applications like hardcover books and architectural drawings. However, it may lack the stiffness of short grain paper, limiting its use for some projects.
How can one prevent printing issues by aligning paper grain direction correctly?
To avoid potential printing problems related to grain direction, ensure to align the paper's fibers correctly. Check packaging labels,
In conclusion, understanding the differences between short grain and long grain paper is crucial. Short grain paper offers advantages in specific applications, while long grain paper excels in others. Identifying paper grain direction is essential for successful printing and bookbinding. Aligning grain direction correctly avoids printing issues. Choose the right paper grain direction based on project requirements. Knowing how grain direction affects handling and binding is key. Avoid common mistakes when working with short and long grain paper for optimal results. Make informed decisions for successful paper usage in printing and bookbinding.