Are Offset Printing Plate Sizes Impacting Your Print Quality?
Understanding Standard Offset Printing Plate Sizes
Offset printing is a commonly used printing technique in the industry, known for its high-quality print results and cost-effectiveness for large print volumes. To ensure optimal results and efficiency in offset printing, it is important to understand the standard offset printing plate sizes and their impact on print quality and productivity.
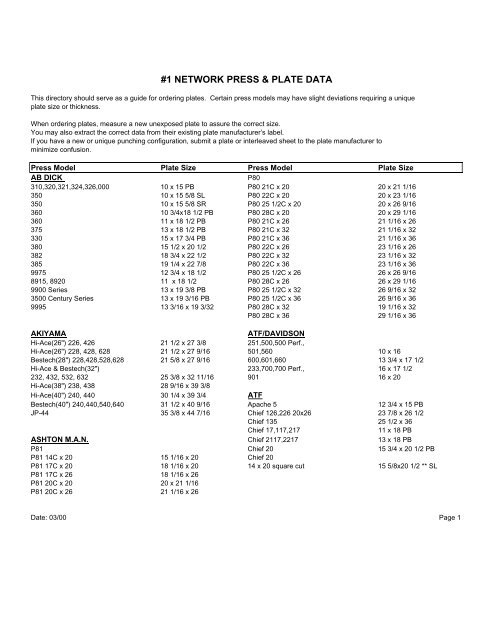
What are the common standard sizes of offset printing plates used in the industry?
In the industry, there are several common standard sizes of offset printing plates. The popular sheetfed offset press plate sizes include 650 x 550 mm, 605 x 745 mm, and 1030 x 800 mm. These sizes are widely used by offset press manufacturers and are considered industry standards. Additionally, common press sheet sizes for offset printing range from 1280 x 1030 mm to 1150 x 950 mm.
How do plate sizes impact print quality and efficiency in offset printing?
Plate sizes play a crucial role in determining print quality and efficiency in offset printing. The size of the printing plate directly affects the size of the image that can be printed on the press sheet. Using the appropriate plate size ensures that the image is aligned correctly on the sheet and prevents image distortion or cropping.
Print quality is also influenced by the resolution and detail that can be achieved on the printing plate. Larger plate sizes generally allow for higher resolution and finer details, resulting in sharper and more vibrant prints. On the other hand, smaller plate sizes may limit the level of detail that can be reproduced accurately.
Efficiency in offset printing is impacted by plate sizes through the utilization of press sheet space. Properly matching plate sizes with press sheet sizes can maximize the number of prints that can be produced in a single run, reducing paper waste and increasing productivity. It also allows for more efficient imposition and layout planning, optimizing the use of materials and minimizing production time.
Materials and Manufacturing Processes of Offset Printing Plates
Offset printing plates are essential components of the offset printing process, responsible for transferring the desired image onto the printing surface. Understanding the materials used in offset printing plates and the manufacturing processes involved provides insights into their durability, accuracy, and suitability for different printing applications.
What materials are offset printing plates typically made of?
Offset printing plates can be made from various materials, including metal, plastic, rubber, and paper. The choice of material depends on factors such as print volume, print quality, and the specific requirements of the printing project.
Metal plates, particularly aluminum plates, are commonly used in the industry due to their durability, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Aluminum plates offer excellent dimensional stability, making them suitable for high-quality prints with precise registration. They are also easy to handle and mount on the plate cylinder.
Plastic plates, such as polyester or polystyrene plates, are often used for low-volume or short-run printing applications. While they may not offer the same level of durability as metal plates, plastic plates can be more cost-effective for certain projects, especially when rapid turnaround times are required.
Rubber plates, also known as flexographic printing plates, are mainly used for flexible packaging and label printing. They are made of rubber materials with photopolymer coatings that allow for quick and easy plate production. Rubber plates are known for their versatility and suitability for various substrates, including uneven or non-porous surfaces.
Paper plates, also known as disposable plates, are generally used for small-scale or temporary printing applications. They are typically made of paper or cardboard materials with a photosensitive coating. Paper plates are less durable compared to other plate materials but can be more economical for short-term or limited-use applications.
How is the manufacturing process of offset printing plates carried out?
The manufacturing process of offset printing plates involves various techniques and technologies depending on the plate material and the desired specifications.
Metal plates, particularly aluminum plates, are typically manufactured through a photochemical or photomechanical process. This process involves applying a light-sensitive coating, often a photosensitive emulsion or polymer, onto the aluminum surface. The coating is exposed to light through a film negative or digital file, creating the desired image on the plate. The plate is then chemically treated to develop the image and remove the unexposed coating, resulting in a ready-to-use printing plate.
Plastic plates, especially polyester or polystyrene plates, are generally produced using a similar photomechanical process. A light-sensitive coating is applied to the plastic surface, and the plate is exposed to light through a film negative or digital file. After exposure, the plate is developed and treated to remove the unexposed coating, revealing the image on the plate.
Rubber plates, or flexographic printing plates, are manufactured using a different process called laser engraving. In this process, a laser beam is used to selectively remove the rubber material, creating the desired image or pattern on the plate. Laser engraving provides precise and accurate results, allowing for high-quality prints with excellent registration.
Paper plates, also known as disposable plates, are typically manufactured through a similar photomechanical process as metal and plastic plates. A light-sensitive coating is applied to the paper or cardboard surface, and the plate is exposed to light to create the image. The plate is then developed and treated to remove the unexposed coating, resulting in a usable printing plate.
Section 3: Optimization and Efficiency in Offset Printing
How can designers optimize print layouts based on standard offset printing plate sizes?
To optimize print layouts based on standard offset printing plate sizes, designers should consider several factors. Firstly, they should carefully select the appropriate plate size that matches the desired print size. By doing so, they can ensure that the image fits perfectly on the plate and allows for precise registration on the press sheet.
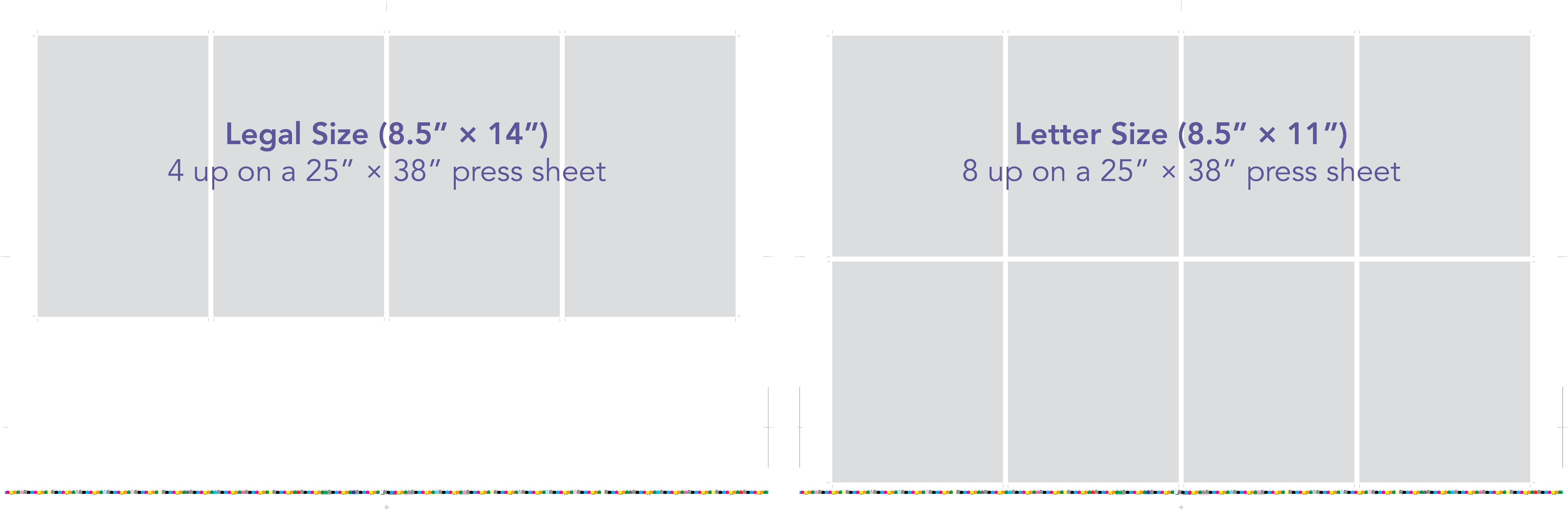
Designers should also consider the imposition or arrangement of multiple prints on a single press sheet. By strategically positioning multiple versions of a project on a single sheet, a technique known as gang printing, they can reduce press sheet usage and minimize costs. This technique is particularly effective for small prints or projects with similar design elements.
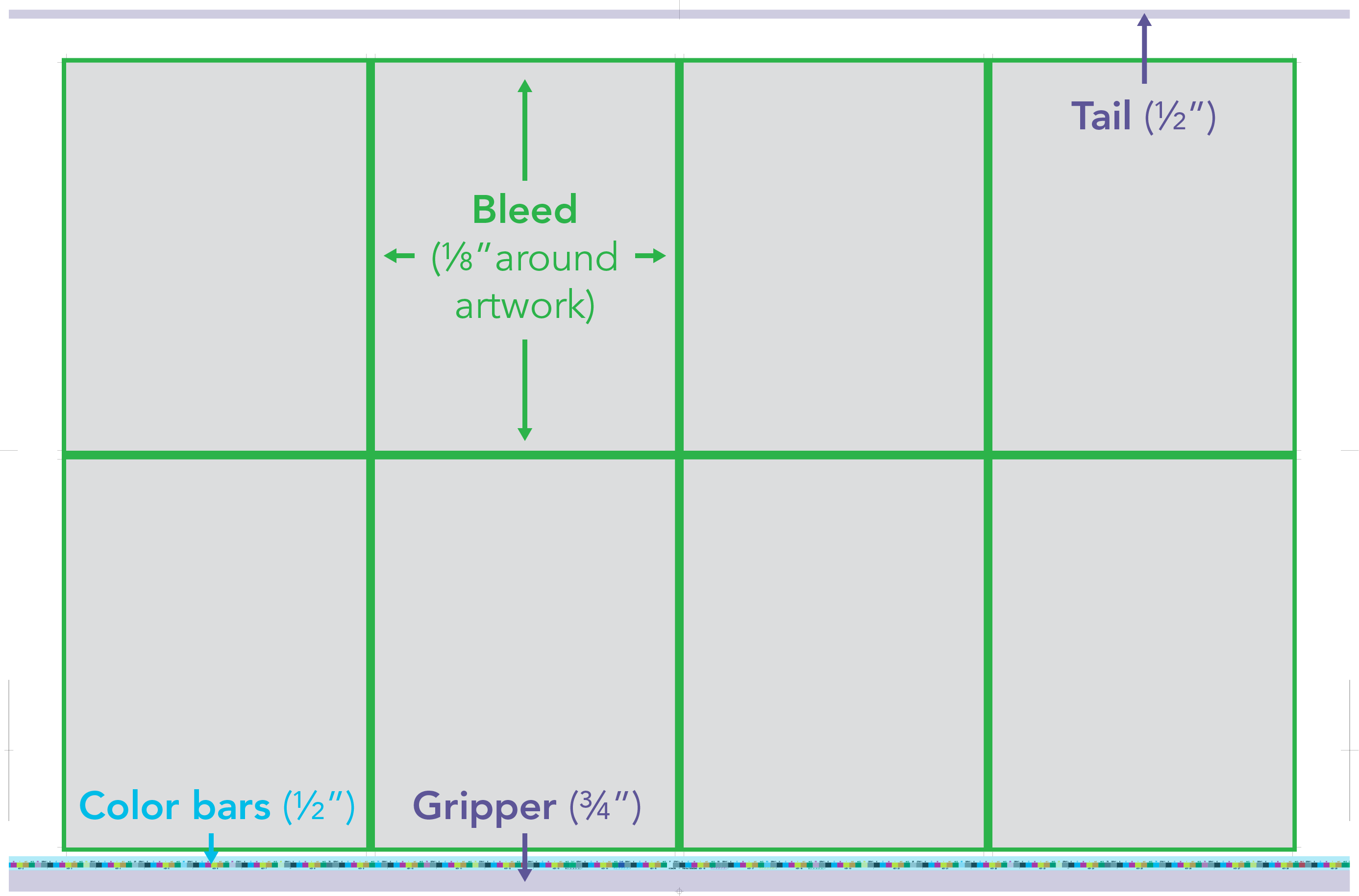
In addition, designers should account for essential elements such as gripper, back edge, color bars, gutters, and bleeds when planning print layouts. By leaving sufficient space for these elements, they can avoid issues such as improper color registration or image cropping. This ensures that the final prints meet the desired specifications and quality standards.
To further visualize the data from this section, let’s create a table to summarize the factors mentioned:
| Factors to Consider for Print Layout Optimization |
|---|
| Select the appropriate plate size for desired print size |
| Strategically position multiple prints on single press sheet |
| Account for essential elements such as gripper, back edge, color bars, gutters, and bleeds |
What factors should be considered to maximize efficiency and minimize waste in offset printing?
Maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste in offset printing involve careful planning and consideration of various factors. One key factor is the correlation between the flat size (print design size) and the press sheet size. Designers should aim to achieve optimal utilization of the press sheet by selecting the appropriate sheet size based on the print design and the desired quantity.
Accounting for elements such as gripper, tail, color bars, and bleeds is essential to ensure proper spacing and alignment on the press sheet. By leaving sufficient space for these elements, designers can avoid printing issues and maintain the desired print quality.
Another factor to consider is the concept of gang printing, as mentioned earlier. By combining multiple versions of a project on a single press sheet, designers can maximize press sheet capacity and reduce waste. This technique is particularly useful when multiple versions of a project share similar design elements or color schemes.
Additionally, designers should consider requesting specialized paper stocks for large quantity orders. By making specific size stock options available, they can further optimize press sheet utilization, minimize waste, and achieve cost-effective printing.
To visualize the data from this section, let’s create a table summarizing the factors for maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste:
| Factors to Maximize Efficiency and Minimize Waste |
|---|
| Correlation between flat size and press sheet size |
| Accounting for elements such as gripper, tail, color bars, and bleeds |
| Utilizing gang printing for multiple versions of a project |
| Requesting specialized paper stocks for large quantity orders |
How does selecting the appropriate plate and press sheet sizes impact the overall production process in offset printing?
Selecting the appropriate plate and press sheet sizes plays a crucial role in the overall production process in offset printing. Properly matching the plate size to the desired print size ensures that the image is accurately reproduced on the press sheet, without any loss of detail or distortion.
Aligning the plate and press sheet sizes enables efficient imposition and layout planning. By optimizing the use of materials and minimizing production time, designers can increase productivity and reduce costs. It also allows for the production of larger quantities of prints in a single run, resulting in faster turnaround times and improved customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, selecting the appropriate plate and press sheet sizes also contributes to minimizing waste. By using the optimal amount of materials, designers can reduce paper waste and reduce the environmental impact of the printing process. This aligns with sustainable printing practices and reflects positively on the company’s image.
To summarize the impact of selecting appropriate plate and press sheet sizes, let’s create a table:
| Impact of Selecting Appropriate Plate and Press Sheet Sizes |
|---|
| Accurate reproduction of image on press sheet |
| Efficient imposition and layout planning |
| Increase in productivity and cost reduction |
| Minimization of waste and environmental impact |
In conclusion, understanding standard offset printing plate sizes, the materials used in their manufacturing, and the optimization and efficiency techniques in offset printing are important for achieving high print quality, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. By leveraging this knowledge, designers and print professionals can deliver exceptional results and maximize the value of offset printing.
With the comprehensive guide provided in this article, readers can gain insights into the intricacies of offset printing plate sizes and make informed decisions in their printing projects. By keeping in mind the importance of standard sizes, material considerations, and efficiency optimization, they can achieve optimal print quality and production efficiency in offset printing.
FAQs about Standard Offset Printing Plate Sizes
What are the common standard sizes of offset printing plates used in the industry?
To determine the common standard sizes of offset printing plates, we consider popular sheetfed offset press plate sizes like 650 x 550 mm, 605 x 745 mm, and 1030 x 800 mm.
How do plate sizes impact print quality and efficiency in offset printing?
In offset printing, plate sizes directly influence print quality and efficiency by determining image alignment, resolution, detail reproduction, and press sheet space utilization.
Why is it important to know the dimensions and specifications of offset printing plates?
Understanding the dimensions and specifications of offset printing plates is crucial for optimizing print layouts, ensuring compatibility across manufacturers, and achieving optimal print quality and production efficiency.
What materials are offset printing plates typically made of?
Offset printing plates can be made from metal (especially aluminum), plastic, rubber (for flexographic printing), or paper, with each material offering unique advantages based on factors like print volume and application requirements.
How can designers optimize print layouts based on standard offset printing plate sizes?
Designers can optimize print layouts by selecting appropriate plate sizes, strategically using gang printing for multiple prints, and accounting for essential elements like color bars, gutters, and bleeds to ensure accurate image reproduction and quality prints.
In conclusion, understanding standard offset printing plate sizes is crucial for print quality. Knowing plate dimensions and materials can optimize efficiency. Designers can maximize efficiency by selecting appropriate plate and press sheet sizes. Offset printing plate sizes play a significant role in the production process. By considering these factors, you can enhance print layouts and minimize waste, leading to improved outcomes in offset printing.