Offset Paper Option: Definition,Types, Uses, and Benefits

What is Offset Paper?
Offset paper is a type of printing paper specifically designed for use in offset printing processes. Produced using pulp, this paper typically has a relatively high weight, usually measured in grams per square meter (GSM). A key characteristic of offset paper is its smoothness, which ensures high-quality prints by allowing excellent ink absorption, resulting in vibrant colors and sharp images. Offset paper can be either coated or uncoated, each offering properties that cater to various printing needs.
Properties of Offset Paper
Offset paper possesses several key properties that make it suitable for a wide array of printing projects. Its weight, typically measured in GSM, determines its thickness and sturdiness, with heavier papers offering better durability. The paper’s smooth surface contributes to its printability, allowing for clean, crisp images and text. High-opacity papers prevent ink bleed-through, ensuring printed materials maintain a professional appearance. Additionally, the brightness and whiteness of offset paper affect color reproduction, making it a versatile choice for various commercial printing applications.
Material Description of Offset Paper
Offset paper is primarily made from wood pulp, processed to create a smooth and even surface suitable for printing. The material is often mixed with additives to enhance properties like brightness and opacity, ensuring the paper meets the demands of commercial printing. Offset paper comes in coated and uncoated finishes, with coated papers offering enhanced smoothness and vibrant color reproduction, while uncoated papers provide a more tactile feel, suitable for projects requiring writing or personalization.
Types of Offset Paper Used in Printing
There are various types of offset paper commonly used in the printing industry, each tailored for specific applications.
Uncoated offset paper
is popular for projects that require a tactile feel, such as letterheads and envelopes. This type of paper allows for easy writing with pens, making it ideal for correspondence.
Coated offset paper
provides a glossy or matte finish, enhancing the vibrancy of colors, making it suitable for brochures and flyers.
Book paper
which is specifically designed for printing books.
Art print paper
which is used for reproducing high-quality images and artwork.
Each type of offset paper has unique properties, including differences in texture, surface characteristics, and weight. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right paper for your specific printing projects, ensuring the best possible results.
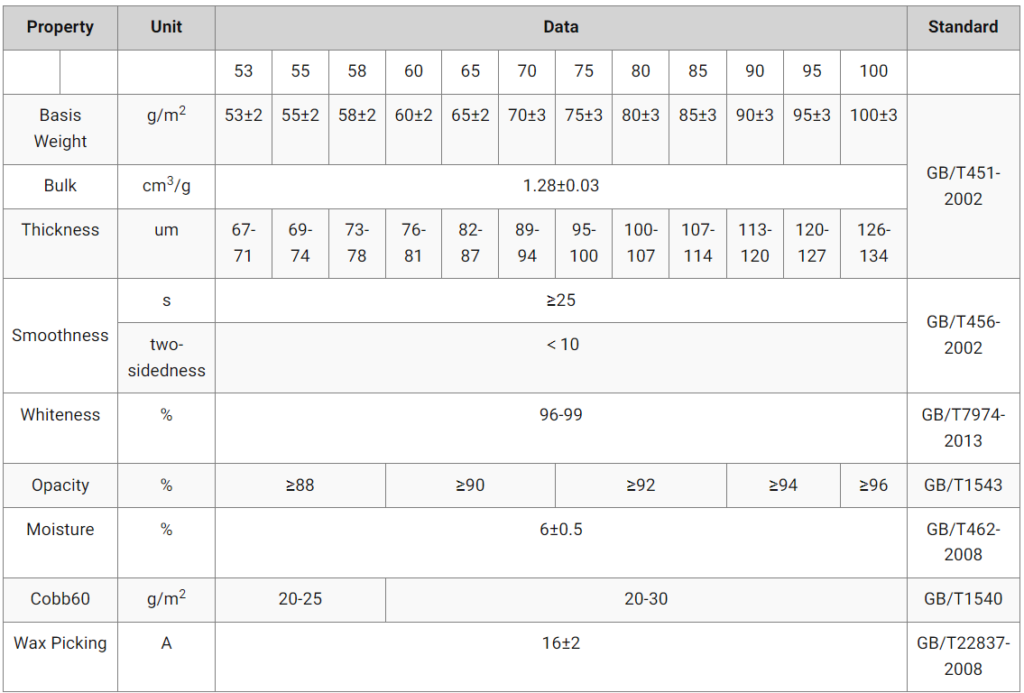
Datasheet of the offsetpaper we offer
Benefits of Using Offset Paper for Printing Projects
Printability
Using offset paper for printing projects offers numerous benefits that enhance the overall quality and effectiveness of the printed materials. One major advantage is its excellent printability, which allows for precise color reproduction and sharp images. When using offset printing techniques, the ink is evenly distributed on the surface of the paper, leading to high-quality results that are often superior to digital printing. This makes offset paper ideal for commercial printing projects where quality is paramount.
Versatility
Another significant benefit is the versatility of offset paper. It can be used for a wide range of applications, from brochures and flyers to business cards and catalogs. The ability to customize the paper’s weight, finish, and texture allows designers to create unique and eye-catching printed materials that effectively communicate their message. Furthermore, offset printing is cost-effective for large runs, making it a preferred choice for businesses looking to produce high-volume prints without sacrificing quality.
How Does the Offset Printing Process Work?
Overview of the Offset Printing Process
The offset printing process begins with the creation of a printing plate, which is made from a metal or polymer material. The image to be printed is transferred onto the plate, and then the plate is mounted onto the printing press. During the printing process, ink is applied to the plate, and the image is then transferred—or offset—onto a rubber blanket roller. From there, the image is finally printed onto the paper. This multi-step process allows for precise color registration and high-quality print results.
After the initial setup, the printing press can produce large quantities of prints quickly and efficiently. The process is highly automated, which ensures consistency across large runs. Each press can be adjusted for different paper weights and sizes, allowing for a variety of printing projects to be completed in one go. Moreover, the offset printing process is particularly effective for large-scale production, which is why it is often favored for commercial printing applications.
The Role of Ink and Paper in Offset Printing
In offset printing, both ink and paper play crucial roles in determining the final print quality. The ink used in offset printing is formulated to adhere well to the surface characteristics of offset paper, ensuring that colors are vibrant and true to the original design. High-quality ink can significantly enhance the print’s brightness and opacity, contributing to an overall polished appearance. The choice of paper also affects how the ink interacts with the surface, making it essential to select compatible materials for the best results.
Another important factor is the ink absorption characteristics of the offset paper. Papers with high ink absorption can lead to faster drying times, reducing the risk of smudging or offsetting onto other pages. Conversely, if the paper absorbs too much ink, it can result in a dull print quality. Therefore, balancing ink properties with the right type of offset paper is essential for achieving high-quality prints that meet professional standards.
Common Printing Methods in Offset Printing
Offset printing employs several common methods, each suited for different types of projects. The most prevalent method is known as sheet-fed offset printing, where individual sheets of paper are fed into the press. This technique is ideal for high-quality prints and smaller runs. Another popular method is web-fed offset printing, which uses a continuous roll of paper, making it perfect for large-volume projects such as newspapers and magazines.
Additionally, there are specialized offset printing techniques, such as letterpress and gravure, which utilize different printing plates and inks to achieve unique effects. Each printing method has its advantages and is selected based on the project requirements, including the desired print quality, volume, and budget. Understanding these methods can help businesses and designers make informed decisions about their printing processes, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their projects.
Choosing the Best Paper for Offset Printing Factors to Consider
When selecting the best paper for offset printing, several factors come into play. The first factor to consider is the type of project you are working on. Different projects have different requirements regarding thickness, weight, and finish. For instance, if you are creating high-quality art prints, a heavier coated paper would be the best choice for vibrant colors and sharp details. Conversely, for everyday printing tasks, uncoated paper might suffice.
Another essential consideration is the ink compatibility of the paper. Some papers absorb ink better than others, which can affect the overall print quality. If you’re using specific inks, it’s crucial to choose a paper that can handle the ink’s properties effectively. Finally, considering the environmental impact of your paper choice is becoming increasingly important. Opting for eco-friendly options can not only benefit the planet but also enhance your brand’s image.
Intended Use, Budget, and Desired Outcome
Understanding the intended use of your printed materials is vital in choosing the right offset paper. For example, if you are designing a promotional flyer, you may want a paper that is lightweight yet durable enough to withstand handling. Conversely, if you’re producing an invitation, a heavier, more luxurious paper can make a lasting impression. Your budget also plays a crucial role in this decision. Balancing cost with quality ensures you achieve your desired outcome without overspending.
Desired outcomes should also be a guiding factor. If you aim for vibrant colors and stunning imagery, a glossy coated paper would be suitable, while a matte finish might be preferred for a more subdued, elegant look. Keep in mind that the type of project will often dictate the appropriate paper characteristics, so aligning your choices with your overall goals will lead to more successful printing results.
Weight/Thickness
The weight and thickness of offset paper are critical attributes that can greatly influence print quality and durability. Paper weight is typically measured in GSM, and choosing the right weight will depend on the specific needs of your project. Heavier papers are often more durable and provide a professional feel, making them ideal for business cards and high-end brochures. Conversely, lighter papers may be more suitable for large volume printing, such as flyers and newsletters, where cost efficiency is key.
Moreover, the thickness of the paper affects its printability. Thicker papers can absorb more ink, which can enhance color vibrancy but may also require adjustments in the printing process. It’s essential to take into account both the weight and thickness when selecting offset paper to ensure that it aligns with your printing needs and project requirements, ultimately contributing to the overall success of your printing endeavors.
Coated vs Uncoated
Choosing between coated and uncoated offset paper is a crucial decision that impacts the final print quality. Coated paper features a smooth finish that enhances color reproduction, making it ideal for projects that require vibrant images, such as brochures and posters. The coating allows for better ink absorption, resulting in sharper and more vivid colors. However, coated papers may not be suitable for writing or projects that require tactile engagement.
On the other hand, uncoated paper offers a more natural feel and texture, making it perfect for letterheads, envelopes, and stationery where writing is involved. This type of paper can also provide a more subtle and sophisticated look, ideal for high-end branding. Understanding the differences between coated and uncoated papers allows designers and printers to make informed choices, tailoring their selections to meet the specific requirements of each project.
Smoothness/Texture
The smoothness and texture of offset paper significantly influence the print quality and the final appearance of printed materials. Smooth papers facilitate even ink distribution, leading to cleaner lines and sharper images. This is especially important for projects like business cards where clarity and professionalism are paramount. The texture can also affect the tactile experience of the printed piece, creating a more engaging interaction for the recipient.
Conversely, textured papers can add depth and interest to printed materials, providing a unique touch that can enhance the overall aesthetic. However, these papers may require specific printing techniques to achieve the desired results, as the texture can affect ink absorption and color fidelity. Therefore, understanding the implications of smoothness and texture is essential when selecting offset paper to ensure the best possible outcome for your printing projects.
Opacity
Opacity is a crucial property of offset paper that determines how much light passes through the paper. High-opacity papers are essential for preventing ink bleed-through, which can compromise the quality of printed materials. This is particularly important for double-sided printing, where images and text need to remain crisp and clear on both sides. If the opacity is insufficient, the printed images may appear washed out or muddled, detracting from the overall design.
When selecting offset paper, consider the opacity ratings to ensure that the paper meets your project requirements. Different types of paper offer varying levels of opacity, so understanding your specific needs is key. For projects requiring high-quality prints, such as brochures and invitations, investing in high-opacity offset paper can make a significant difference in the final product’s appearance and quality, enhancing the overall effectiveness of your printed materials.
Brightness/Whiteness
The brightness and whiteness of offset paper are vital factors that influence print quality and color accuracy. Papers with higher brightness levels tend to produce more vibrant colors and sharper contrasts, making them ideal for projects that require eye-catching visuals. Bright white papers often enhance the overall appearance of printed materials, contributing to a more professional look. This is particularly important for marketing materials, where first impressions can significantly impact a potential client’s decision.
Additionally, the whiteness of the paper affects how colors are perceived when printed. Papers with a bluish tint may enhance cooler colors, while those with a warmer tone can bring out warmer hues. Selecting the right level of brightness and whiteness is essential for achieving the desired color fidelity in your printed projects, ensuring that the final outcome aligns with your creative vision and meets professional standards.
Ink Compatibility
Ink compatibility is a critical consideration when choosing offset paper, as it directly influences print quality and durability. Different inks behave uniquely on various types of paper, affecting absorption rates and color vibrancy. It’s essential to select offset paper that works well with the specific inks you plan to use, whether they are water-based, oil-based, or UV inks. Proper ink-paper compatibility ensures that the ink adheres correctly, resulting in sharp, clear images and text.
Moreover, understanding the paper’s surface characteristics can greatly impact ink performance. Coated papers typically have higher levels of ink absorption, which can enhance color vibrancy, while uncoated papers may require specific inks to achieve optimal results. By considering ink compatibility when selecting offset paper, designers and printers can ensure that their projects yield the best possible outcomes, resulting in high-quality printed materials that effectively convey their intended message.
What is the Importance of Paper Weight in Offset Printing?
Paper weight plays a crucial role in offset printing, influencing both the final product and the overall printing process. The weight of paper is measured in basis weights, which determine its thickness and sturdiness. For color printing, a paper with a high weight can enhance sharpness and saturation, resulting in an excellent print quality. Conversely, papers with lower weight may produce a smear effect, especially when using high-speed printers. Choosing the right stock used is equally important; environmentally friendly paper options, like biodegradable or FSC and PEFC-certified papers, help reduce the carbon footprint while maintaining premium quality.
For manual and digital printing purposes, the surface smoothness and gloss of the paper also matter. Vellum and coarse stocks can yield different aesthetics, making them suitable for various applications. Small and medium businesses must consider these factors when selecting paper, as they want to minimize costs while ensuring an appealing presentation. This leads to frequently asked questions regarding the best weight of paper for specific projects. In conclusion, understanding paper weight and its properties is essential for achieving the desired results in offset printing.
What are Common Applications of Offset Paper?
Offset paper is widely utilized in various industries due to its versatility and quality. These papers are commonly used for printing tasks that require precision, such as brochures, flyers, and magazines. The paper has a relatively smooth surface, ensuring that printed images and text appear sharp and vibrant. This is particularly important for products that aim to elevate brand appeal.
Moreover, offset paper is often produced using environmentally responsible practices, such as sourcing from PEFC and Forest Stewardship Council certified forests. This means that the materials used, including spruce, come from renewable resources. Additionally, the manufacturing process can involve bleach, which is used to achieve a shiny finish that enhances the visual quality of printed materials.
Furthermore, offset paper is frequently used for packaging materials, where its durability is crucial. The ISO standards ensure that these papers meet specific quality benchmarks, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether being printed on with a ballpoint pen or utilized for high-quality printing, offset paper remains a staple in the industry.

Publishing
Ideal for books, magazines, newspapers, and catalogs due to its durability and high-quality print results.

Advertising
Used for brochures, flyers, posters, and promotional materials to showcase vibrant colors and detailed graphics.

Corporate Printing
Commonly used for letterheads, business cards, envelopes, and corporate stationery for a professional look.

Packaging Inserts
Suitable for packaging inserts, product manuals, and instructional materials requiring clear and crisp printing.

Direct Mail
Used for direct mail marketing campaigns, offering a combination of durability and print quality to convey promotional messages effectively.

Educational Materials
Preferred for textbooks, workbooks, and educational resources where readability and longevity are essential.

Stationery
Used for stationery items such as notepads, memo pads, and letter sets for a premium look and feel.

