Why Is Consumer Demand for PLA Coated Paper Rising?
What is PLA Coated Paper and Why is Consumer Demand Increasing?
Introduction to PLA Coated Paper
PLA (Polylactic Acid) coated paper is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic-coated paper. It is made from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, making it biodegradable and compostable. The PLA coating provides a water-resistant barrier, making it suitable for various food packaging applications.
Definition and Composition
PLA coated paper is a type of food-grade paper that is coated with a PLA film. PLA, also known as polylactic acid, is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources. It is made by fermenting sugars found in cornstarch or sugarcane into lactic acid, which is then polymerized to form PLA.
The PLA film is applied to the base paper, such as kraft, white, or bamboo paper, through a laminating process. The coating provides a barrier against moisture and grease, ensuring the paper remains durable when in contact with food or beverages.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of PLA coated paper involves several steps. First, the PLA film is produced by polymerizing lactic acid into PLA pellets. These pellets are melted and extruded onto a casting drum, forming a thin film. The film is then stretched and cooled to improve its mechanical properties.
Next, the base paper is fed through a laminating machine, where the PLA film is applied to one or both sides of the paper. The coated paper is then dried and wound into rolls. Depending on the specific application, additional processing steps such as printing, cutting, and shaping may be performed to create the final product.
Eco-Benefits of PLA Coated Paper
One of the key reasons for the increasing consumer demand for PLA coated paper is its eco-friendly nature. Compared to traditional plastic-coated paper, PLA coated paper offers several environmental benefits.
Biodegradability and Compostability
PLA coated paper is 100% biodegradable and compostable. When disposed of in the proper composting conditions, it can break down naturally within 6-12 months. The PLA coating decomposes into carbon dioxide and water, leaving behind no harmful residues.
This biodegradability is a significant advantage over petroleum-based plastics, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years. PLA's ability to biodegrade and become part of the natural carbon cycle aligns with global sustainability goals and reduces reliance on non-renewable resources.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gases and Energy Consumption
The production of PLA coated paper has a lower carbon footprint and reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional plastic-coated paper. PLA is derived from renewable resources and requires 65% less energy to produce. It also generates 63% fewer greenhouse gases during manufacturing, further contributing to a reduced environmental impact.
Additionally, PLA coated paper production involves a lower energy consumption process compared to traditional polyethylene (PE) coatings. This energy efficiency helps to conserve resources and reduce the carbon footprint associated with paper manufacturing.
How Does PLA Coated Paper Compare to Traditional Materials?
[Keyword Cluster]= PLA vs Traditional Paper, Biodegradable Packaging, Eco-Friendly Packaging
Comparative Analysis with Polyethylene (PE)
When it comes to packaging materials, traditional materials like polyethylene (PE) have been widely used. However, PLA coated paper offers several advantages over PE in terms of its environmental impact, recyclability, and cost considerations.
Environmental impact and recyclability
PLA coated paper is considered a more sustainable option compared to PE, as it is made from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. In terms of production, PLA requires 65% less energy and generates 63% fewer greenhouse gases compared to petroleum-based plastics. This lower carbon footprint makes PLA a more eco-friendly choice.
Furthermore, while PE is not biodegradable, PLA coated paper is fully compostable. Under specific composting conditions, it can break down into non-toxic substances within 6-12 months. However, it's important to note that PLA does require industrial composting facilities for proper degradation, as it does not readily decompose in typical home compost piles or landfill environments.
Cost considerations
In terms of cost, PLA coated paper may have a higher upfront price compared to PE. However, as production efficiencies improve and more manufacturers adopt PLA, the cost gap is expected to narrow down. Additionally, the long-term cost benefits of PLA, such as reduced environmental impact and potential savings in waste management, make it an attractive option for businesses looking to improve their sustainability practices.
Benefits and Limitations of PLA Coated Paper
While PLA coated paper offers several benefits, it is important to consider its limitations as well.
Shelf life and heat sensitivity
One of the limitations of PLA coated paper is its relatively short shelf life. Depending on the specific product and storage conditions, PLA coated paper may only have a shelf life of 6 months or less. This makes it unsuitable for long-term packaging solutions or products that require extended storage or shipping, especially for export purposes.
Additionally, PLA has a lower heat resistance compared to traditional PE coatings. While PE can withstand temperatures up to 120°C, PLA's heat resistance limit is around 70°C. This means that PLA coated paper may soften or deform when exposed to hot liquids or high temperatures, limiting its suitability for certain applications.
Applications in food packaging
Despite its limitations, PLA coated paper has gained popularity in the food packaging industry due to its unique advantages. PLA's water resistance makes it suitable for packaging hot beverages and take-out food containers, as it prevents the paper from becoming weak or soggy when exposed to moisture. This water resistance property is achieved through the PLA coating, which forms a barrier between the paper and the contents inside.
In terms of food safety, PLA coated paper meets FDA food-grade standards and does not release harmful chemicals when in contact with food. This makes it a reliable and safe option for food packaging.
Consumer Preferences and Brand Considerations
Consumer preferences and environmental considerations have a significant impact on the demand for PLA coated paper. With a growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly practices, consumers are increasingly looking for packaging options that align with their values.
Brands that adopt PLA coated paper for their packaging can benefit from a positive brand perception. By showcasing their commitment to sustainability and reducing their environmental impact, brands can build trust and loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers.
Several case studies highlight the positive impact of adopting PLA coated paper on brand perception. For example, a famous coffee chain that switched from traditional PE-coated cups to PLA coated cups experienced an increase in customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. By actively promoting their sustainable practices, the brand successfully attracted environmentally conscious consumers and positioned themselves as an eco-friendly choice in the market.
Life Cycle Analysis and Environmental Impact
To fully understand the environmental impact of PLA coated paper, it is essential to consider its life cycle assessment and long-term sustainability benefits.
Lifecycle assessment data
A life cycle assessment (LCA) provides a comprehensive analysis of the environmental impact of a product from its production to its disposal. LCAs take into account factors such as energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
Based on available data, PLA coated paper has a lower impact on the environment compared to traditional PE-coated paper. The renewable nature of PLA and its reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during production contribute to its overall eco-friendliness.
Long-term sustainability benefits
Furthermore, the use of PLA coated paper supports long-term sustainability goals. By reducing dependency on non-renewable resources and promoting compostability, PLA coated paper contributes to a circular economy where resources are used efficiently and waste generation is minimized.
To maximize the sustainability benefits of PLA coated paper, it is crucial to ensure proper infrastructure for the composting of PLA products. This includes the availability of industrial composting facilities and consumer education on the proper disposal and composting of PLA-coated items.
In conclusion, PLA coated paper offers several advantages over traditional materials like PE in terms of its environmental impact, recyclability, and cost considerations. While PLA has certain limitations, such as its shelf life and heat sensitivity, its benefits in terms of compostability, water resistance, and food safety make it an attractive option for a wide range of food packaging applications. With increasing consumer demand for sustainable packaging options, PLA coated paper can play a crucial role in reducing plastic waste and promoting eco-friendly practices in the packaging industry.
Future Trends and Challenges in the PLA Coated Paper Market
PLA coated paper, also known as polylactic acid coated paper, is gaining traction in the market as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic-coated paper. As consumer awareness about environmental issues continues to grow, the demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions like PLA coated paper is increasing. In this section, we will explore the future trends and advancements in the PLA coated paper market, as well as the challenges that the industry faces. We will also discuss strategies for increasing consumer awareness and supporting the adoption of PLA coated paper.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The production of PLA coated paper relies on advancements in PLA production methods. To meet the increasing demand for PLA coated paper, manufacturers are continually improving the efficiency and scalability of their production processes. Through innovations in polymerization, extrusion, and lamination, PLA producers are working towards reducing costs and increasing the availability of PLA materials.
Furthermore, there are ongoing research and development efforts to explore future applications of PLA coated paper beyond food packaging. PLA’s versatility and biodegradability make it a promising material for various industries such as healthcare, cosmetics, and textiles. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see PLA coated paper being used in a wider range of products.
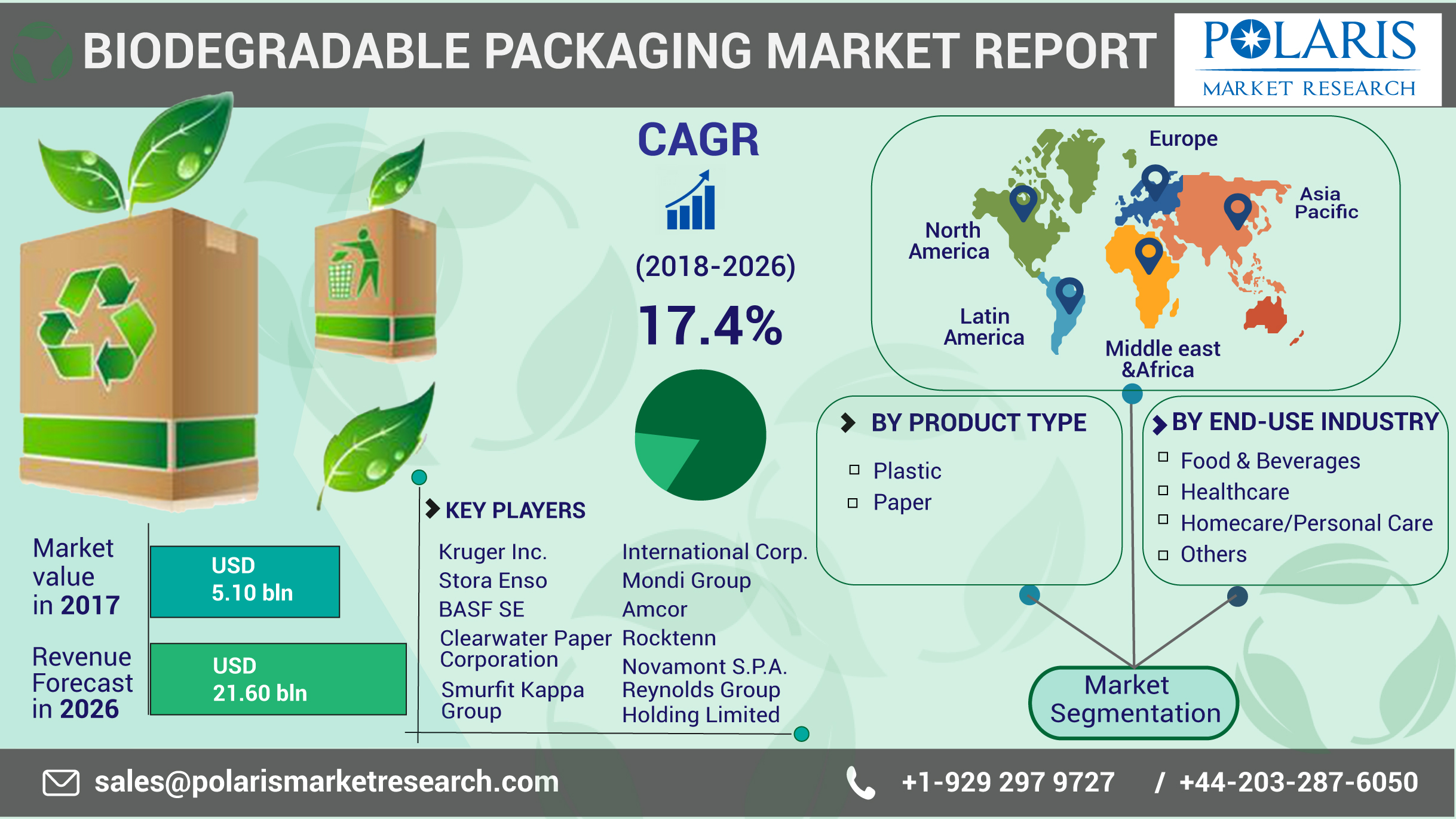
Market Growth and Projections
The PLA coated paper market is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years. According to market research, the global PLA market is projected to reach a value of $2.9 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including increasing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions and government initiatives promoting eco-friendly practices.
Government policies and incentives also play a crucial role in driving the growth of the PLA coated paper market. Many countries are implementing regulations and targets to reduce plastic waste and promote the use of renewable and recyclable materials. Incentives and subsidies offered by governments further encourage manufacturers to invest in PLA production and adopt sustainable practices.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
While PLA coated paper offers many benefits, there are still challenges and barriers that need to be addressed for wider adoption. One of the main challenges is the limited availability of industrial composting facilities. PLA requires specific conditions and temperatures for proper degradation, and industrial composting facilities with the necessary infrastructure are not universally accessible. This limitation restricts the disposal options for PLA coated paper and can hinder its environmental benefits if it ends up in landfills instead of composting facilities.
Another consideration is the ethical implications of using crop resources for PLA production. PLA is primarily made from cornstarch or sugarcane, which can raise concerns about the impact on global food supply and prices. With millions of people worldwide facing food insecurity, there is a need to carefully balance the use of crops for packaging materials against the need for food production.
Strategies for Increasing Consumer Awareness
To support the adoption of PLA coated paper and increase consumer awareness, various strategies can be implemented. Education initiatives and campaigns are essential for raising awareness about the benefits of PLA coated paper and its proper disposal methods. Informative materials, such as brochures, websites, and videos, can help consumers understand the environmental impact of different packaging materials and make informed choices.
Collaboration between stakeholders is also crucial. Manufacturers, retailers, and consumers need to work together to create a sustainable packaging ecosystem. This can involve sharing best practices, engaging in research and development efforts, and collaborating on infrastructure development for composting. Public-private partnerships can play a significant role in driving the transition to more sustainable packaging solutions.
Additionally, infrastructure development for composting is essential to ensure that PLA coated paper can be properly disposed of and composted in industrial facilities. Investments in composting facilities and the establishment of collection systems will support the growth of the PLA coated paper market by providing the necessary infrastructure to handle the disposal of PLA products.
In conclusion, the future of the PLA coated paper market looks promising, with advancements in technology and growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions. However, challenges related to composting infrastructure and ethical considerations need to be addressed. By implementing strategies for increasing consumer awareness and investing in the necessary infrastructure, the adoption of PLA coated paper can be further supported, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Table 1: Comparison between PLA Coated Paper and Polyethylene (PE)
| Aspect | PLA Coated Paper | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, biodegradable, compostable | Higher carbon footprint, not biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, potential long-term cost benefits | Lower upfront cost |
| Shelf Life | Relatively short shelf life | Longer shelf life |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance compared to PE | Higher heat resistance |
Table 2: Market Projections for PLA Coated Paper
| Year | Value (in billions) | CAGR |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | $X.X | – |
| 2022 | $X.X | X.X% |
| 2023 | $X.X | X.X% |
| 2024 | $X.X | X.X% |
| 2025 | $X.X | X.X% |
| 2026 | $2.9 | 17.5% |
FAQs about Consumer Demand for PLA Coated Paper:
What is PLA coated paper?
PLA coated paper is an eco-friendly food-grade paper coated with polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable polymer made from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane.
What are the environmental benefits of PLA coated paper?
The environmental benefits of PLA coated paper include being 100% biodegradable and compostable, meaning PLA coated paper can decompose into carbon dioxide and water within 6-12 months under composting conditions.
How does PLA coated paper compare to traditional plastic-coated paper?
Compared to traditional plastic-coated paper, PLA coated paper requires 65% less energy to produce, generates 63% fewer greenhouse gases, and is made from renewable resources, making it a more sustainable packaging option.
Why is consumer demand for PLA coated paper increasing?
Consumer demand for PLA coated paper is increasing due to growing environmental consciousness and regulatory measures that promote the use of sustainable and biodegradable packaging alternatives.
What are some limitations of PLA coated paper?
Some limitations of PLA coated paper include a relatively short shelf life of around 6 months and a lower heat resistance of up to 70°C, which can affect its suitability for long-term or high-temperature applications.
In this blog post, I discussed PLA coated paper, its eco-friendly perks, and rising demand. Consumers want greener options due to climate concerns and stricter laws. Comparing PLA with traditional materials shows clear environmental benefits despite some limitations. Future trends point to innovations and market growth, though challenges like composting facilities need tackling. PLA coated paper is the future of sustainable packaging, but education and infrastructure must keep pace.